|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Constituents Tab |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Constituents Tab |
  
|
This tab is used to specify the constituents for the concrete mix design.
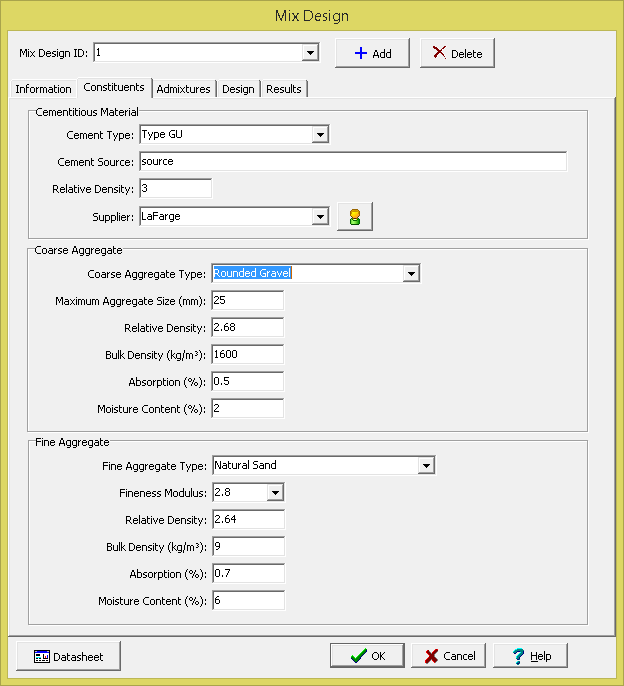
The following information can be specified on this tab:
Cementitious Material
Cement Type: This is used to select the type of cement in the mix design. The type of cement is selected from a list of previously specified cement types.
Cement Source: This is used to specify the source of the cement.
Relative Density: This is used to specify the relative density of the cement. The relative density is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Supplier: This is used to select the supplier of the cement. The suppler is selected from a list of previously specified suppliers. If the button on the right of the supplier is clicked a form will be displayed show the supplier contact and address information.
Coarse Aggregate
Coarse Aggregate Type: This is used to select the type of coarse aggregate. Coarse aggregate types are selected from a list of previously defined coarse aggregate types. The water content of the concrete is influenced by the aggregate size, shape and texture. When the type of coarse aggregate is selected the water reduction from coarse aggregates is also specified in the previously defined list..
Maximum Aggregate Size: This is the maximum size of the coarse aggregate. The maximum aggregate size along with the exposure is used to provide recommendations for the air content of the mix. Along with the slump, the maximum aggregate size is used to determine the mixing water requirements of the concrete. In addition, in combination with the fineness modulus the maximum aggregate size is used to determine the bulk volume of the coarse aggregate.
Relative Density: This is the relative density of the coarse aggregate. The relative density is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Bulk Density: This is the bulk density of the coarse aggregate. The bulk density is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Absorption: This is the absorption level of the coarse aggregate. It is typically in the range of 0.2% to 4%. The absorption is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Moisture Content: This is the moisture content of the coarse aggregate. The moisture content is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Fine Aggregate
Fine Aggregate Type: This is used to select the type of fine aggregate. Fine aggregate types are selected from a list of previously defined fine aggregate types.
Fineness Modulus: This is used to select the fineness modulus of the fine aggregate. It is used for determining the bulk volume of the coarse aggregate.
Relative Density: This is the relative density of the fine aggregate. The relative density is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Bulk Density: This is the bulk density of the fine aggregate. The bulk density is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Absorption: This is the absorption level of the fine aggregate. It is typically in the range of 0.2% to 2%. The absorption is used in determining the proportions of constituents.
Moisture Content: This is the moisture content of the fine aggregate. The moisture content is used in determining the proportions of constituents.