|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Non-linear Sorption |
  
|
|
<< Click to Display Table of Contents >> Non-linear Sorption |
  
|
In addition to linear sorption, there are two types of non-linear sorption can be modeled. These are Freundlich or Langmuir, the theory for these types is described in the Introduction.
To add this feature check the Non-linear Sorption box on the Special Features tab. The Non-linear Sorption form will be shown on the right side of the tab.
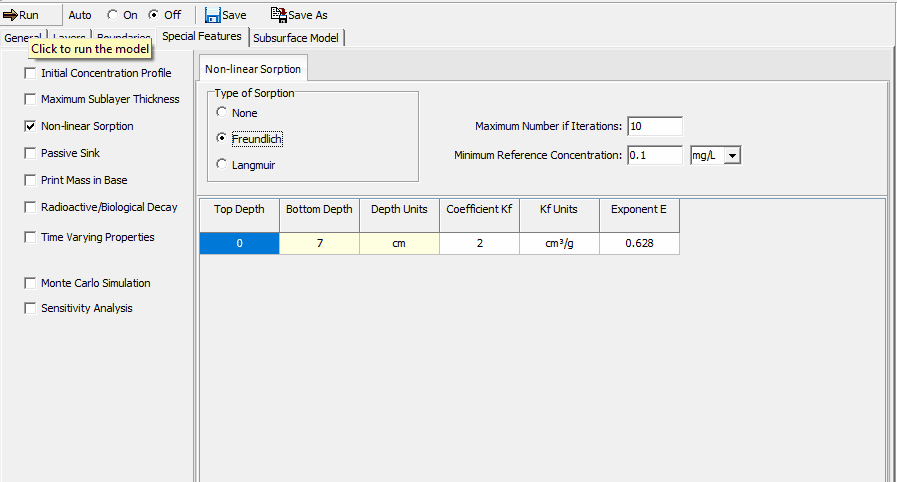
The following can be specified:
Sorption Type: This can be either None, Freundlich, or Langmuir. The layer data will depend on the type of sorption selected.
Maximum Number of Iterations: The iterative procedure used to determine K, repeats until either the maximum change in concentration between iterations is less than 0.1% or the maximum number of iterations is reached.
Minimum Reference Concentration: This is the minimum value that will be used when calculating the secant (linear) distribution coefficient, K. If the average concentration in the sublayer is less than this value, then the Reference value is used.
Freundlich Non-linear Sorption
The following can be entered for each layer specified on the Layers tab.
Coefficient Kf: This is an empirically determined parameter for the layer.
Exponent E: This is an empirically determined parameter for the layer
Langmuir Non-linear Sorption
The following can be entered for each layer specified on the Layers tab.
Parameter Sm: This is an empirically determined parameter for the layer.
Parameter b: This is an empirically determined parameter for the layer.